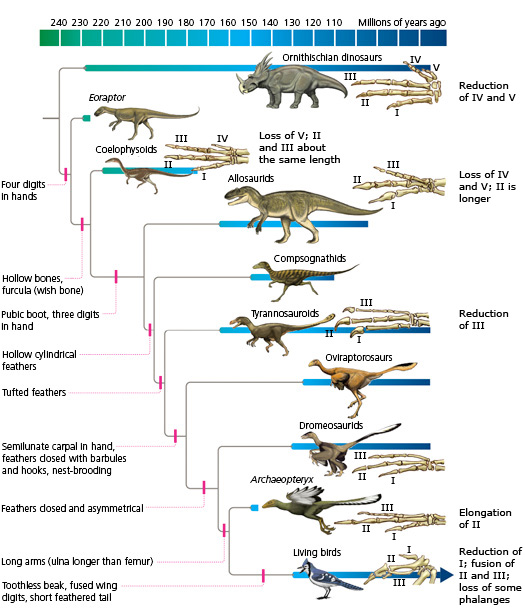

The evolution of birds began in the Jurassic Period, with the earliest birds derived from a clade of theropoda dinosaurs named Paraves.[1] Birds are categorized as a biological class, Aves. For more than a century, the small theropod dinosaur Archaeopteryx lithographica from the Late Jurassic period was considered to have been the earliest bird. Modern phylogenies place birds in the dinosaur clade Theropoda. According to the current consensus, Aves and a sister group, the order Crocodilia, together are the sole living members of an unranked "reptile" clade, the Archosauria. Four distinct lineages of bird survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago, giving rise to ostriches and relatives (Paleognathae), ducks and relatives (Anseriformes), ground-living fowl (Galliformes), and "modern birds" (Neoaves). Phylogenetically, Aves is usually defined as all descendants of the most recent common ancestor of a specific modern bird species (such as the house sparrow, Passer domesticus), and either Archaeopteryx,[2] or some prehistoric species closer to Neornithes (to avoid the problems caused by the unclear relationships of Archaeopteryx to other theropods).[3] If the latter classification is used then the larger group is termed Avialae. Currently, the relationship between dinosaurs, Archaeopteryx, and modern birds is still under debate.