>
Thrid page
<
Frist page
Diffent Types of Stars
What powers a star?
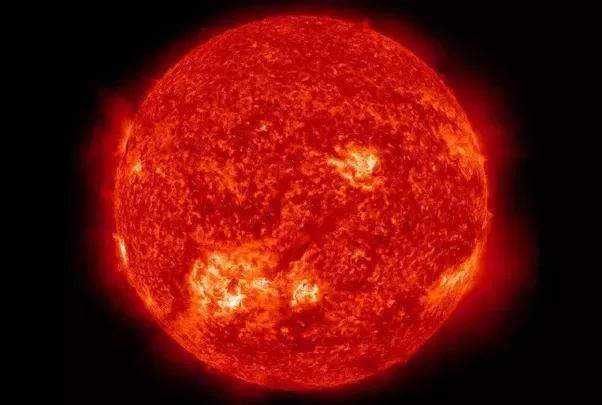
Sometimes people say stars including our sun are giant balls of burning hydrogen this is however one hundred percent false
well the sun like all are star are very, very hot and hygiene tis a very flammable gas one of the key ingredients in fire is oxygen
there are is no oxygen in space so stairs can not simple lite hydrogen on fir to produce energy. instead stars prodec anery though
nuclear fusion. nuclear fusion is the focusing of atoms into heavier elements if this sounds familiar like say something similar to
what goes on inside the rectures of nuclear power plants that because it is well sort of it's more like a relation to what goes on in a
nuclear reactor it's actually the exact opposite nuclear reactors use fission the process of splitting atoms both produce lots of energy but
fusion is a lot more stable and controllable than fission. fusion recourse a great deal of pressure on atoms to take place which stars
do with their gravity.
Why don't stars miploed?
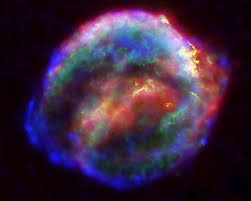
With so much gravity on stars it seems like they would be way denser than they already are even though stars are already really
dence stars aren't so why don't aren't they? the answer is actually fairly straight fared a lot more than you'd expect it to be. See
weel the star's gravity by itself is enough to condec it a lot more to what they exactly in very very large stars the energy produced
by the fousen at a star's core radiates outrides pushouts against the star's gravity many a delicate balance. infect the way stars die is
when that balance balance is disturbed but more on that later
Are there different types of Stars?How many are there? What are they? What defines them?
There are many different types of stars each with their characteristics but the main thing that determine a star's type are
determines a star's type are its age, its mass and its energy output. (not including types of dead stars which will be shown of
page three
In the case of our sun it is a main sequence star which are about 90% of the stars that you can see in the night sky but like all stars in wasn't always one
the sun like all main sequence stars the sun went though the first is the stage protostar.
Protoe Stars
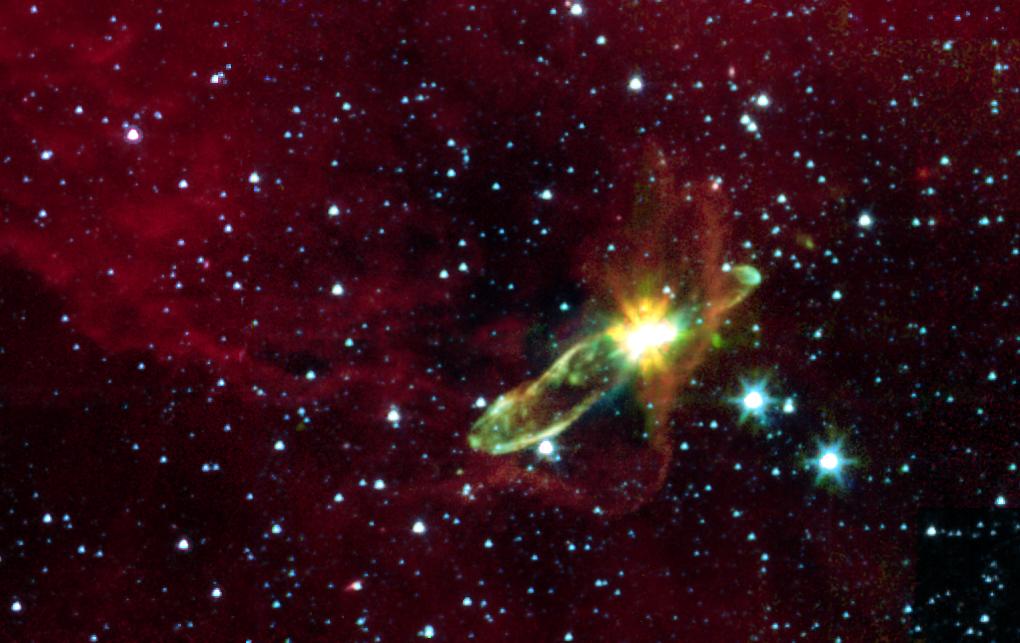

Protostars stars are large collections of gas that has been gathered from nebulas gigantic gas clouds sometimes stretching the furthest reaches of our sailor
systems which can sometimes be some the deaths of old stars that has been pulled to a central location the protostar and has began condensing into a star
but has not yet condensed enough to have engaged pressure for fusion yet.
T Tauri Stars

the second is T Tauri Stars they have begun to condense but do not not yet have to pressure for fusion but produce energy and heat from from
their on going collapsing into a star.
Main sequence stars

Then there are main scene stars like our sun a yellow dwarf our sun is actually an average size star but for some reason average stars are called dwarf don't ask
me why along with smaller stars main sequence stars are sometimes subdivided into yellow and orange dwarfs but are similar enough to each other for both to
just be considered main sequence stars.
Bule Gaient Stars

Blue giant stars are very rare stars that are post main sequence stars. unlike our sun which is still fusing hydrogen blue giants have run out of hydrogen
to focus and began focusing helium the byproduct of hydrogen fousen. fusing helium forces more energy than hydrogen fousen and the souich over from
hydrogen fuses to helium fusion is a sudden one (student in terms of a star's life is a realy realy realy realy realy relay REALY long time form a human perspective)
causing the balance between the star's gravity and the fusion energy at the core to shifted into the cores faver and the little hygen that left to fouse is in the outer
shell of the core. Theres two things cause the star to expand and become much hotter and much bigger than they originally were. if the star has enough mass
to start with the increase in heat causes to be so hot it to glows a very bright blue in color really really big blue giants can become subdivided into blue super
giants however the mass that is recouped to make a blue giant is already super are and with blue supergiants being themselves being rare wine by blue giants
standards the classes of blue supergiant are is offended by many sients not considered to be a real class of star.
Red Giant Stars

Red giant stars are uncommon but are still way way more common than blue giants red granites are also post main sequence stars in fact the sun will become a red
giant star and most go through very similar steps to blue giants some are almost identical to some of the steps of a blue giant however unlike a blue giants red giants
do not have the mass for the enish shullflucionwion of energy to heat the star up enough to cause the star to glow blue so then heat up bit then cool back down to
red quickly then instead give off a generally red but can sometimes be orangish color but still close enough to color to red to be call red but other then that the process
that creates most red giants and blue giants are almost idetaclescome from blue.
Red Super Giant stars

Red supergiants are the largest of all they come from from blue giant stars the girth of from the core catches energy surge that comes from when a blue giant is born
cause the heat to spread out and the star to become a cooler temperature over all resulting in a red color a star that reaches a red supergiant not fouse hilum but then
carbon, neon, oxygen silicon and finally iron. Some scientists consider the largest members of this group into a subdivision called Red Hypergiants.
Red Dawrf Stars

Red dwarf stars are the smallest you can't see any in night sky at all and the longest living stars in the universe red dwarfs are the verge of being a star and a brown dwarf which aren't stars at all and they
can liver for millions of years in fact not only are all the red dwarfs ever created still alive but are still infects. the reason for their long lives is that unlike all other
star types where they only focus in their course red dwarfs found throughout the entire star making their energy output very very small. this makes them very dim
which is why you can't see them in the sky but they are there in fact 60% of stars are red dwarfs
When a Star Dies
There are three things that can happen when a star dies black hole will be talked about on the next page. when a star big enough to become neutron star or black
dies it results in a supernova explosion
The fate of most star including our sun is to become a white dwarf and white dwarfs are created when a low to intermediate mass star runs out of helium unlike larger stars stars like our sun do not go on to
fourier helium so when they run out of helium they lose their outer layers long with half of its original mass in a nebula leaving what's left over
of its former core or a white dwarf. white dwarf are very very hot but they are no longer focusing anything any more or do anything
to generate any heat at all real so why re they so hot you may ask? well what might come a a surprise to some of you is that space
is actually a great insulator tru the temperature of space is as cold anywhere can naturally get but heat generally needs some sort of median
to escape and because pace is well almost entirely empty space that meaning does not exist so the only way for a white dwarf to
louse heat is to radiate it which is a very slow process. so all of the heat in a white dwarf is heat that's left over from when the white
dwarf was star, in fact it takes trillions of years for a white dwarf to cool off completely into a black dwarf (a black dwarf is a white
dwarf that lost all of its heat and turns from a bright white color to black) so every white dwarf that's been created is still around
today
Nutron stars

neutron stars are created when a star with a least around three times the mass of our sun dies its atoms condense into a very
wird configuration. when a star big enough fouse element all the way up to Iron it wiches an issue because the stars doe not get
any energy out of making Iron unlike all the other element before it. as the stars energy producing elements continue to deplete
the stars balance between gravity and the energy from the core pushing outwards continues to shift in gravity's vavier making the
star unstable. Then finally the energy at from the star's core becomes too weak to stava off the star's gravity it implodes causing a supernova. faster
then the human eye can blink it condenses into a size tinier than it ever was in fact some neutrons stars which again need to be at least
three times more massive than the sun to exist can be the size of about mount everest. neutron stars are so dense they are the second
densest things in the universe behind black holes which are in a whole other level entirely. neutron stars very hot and can have extremely fast
rotation speeds especially if they have a smaller neutron star or star feed off of, one neutron star PSRJ1748-2446ad spins at an average of about
24% of the speed of light! however possibly the most energy part of neutron star is that you could compare a neutron star to a very very very
very very very VERY large atom
















